BlueOS SGP-Tools
A BlueOS Extension for Autonomous Approximate Bathymetric Surveys
What Does It Do?
Autonomous Surface Vehicles (ASVs), such as the BlueRobotics BlueBoat, are well-suited for bathymetric surveys. However, it is often the case that an exhaustive survey mapping the depth at every location in an area is infeasible or unnecessary. In such cases, we can leverage variations in the underwater terrain to determine a few critical locations for data collection, which would result in a good approximation of the area's bathymetry.
The SGP-Tools python library provides path planners to address the above problem, known as the informative path planning problem. The BlueOS SGP-Tools extension uses this library to determine ideal locations for the ASV to collect data and controls the ASV to autonomously visit the selected locations.
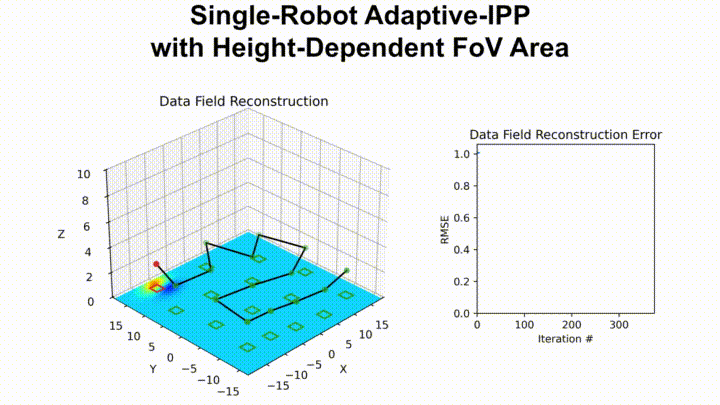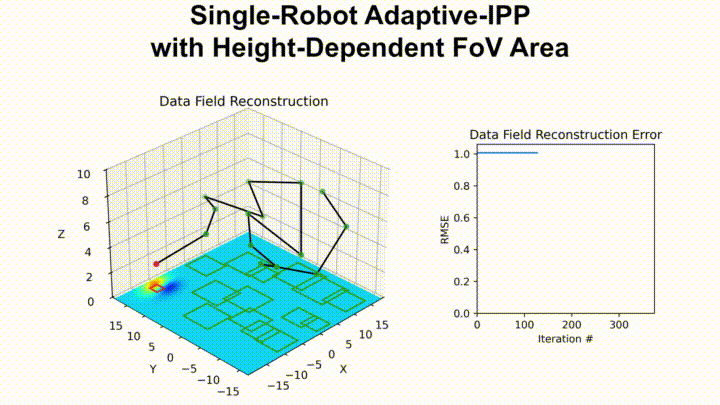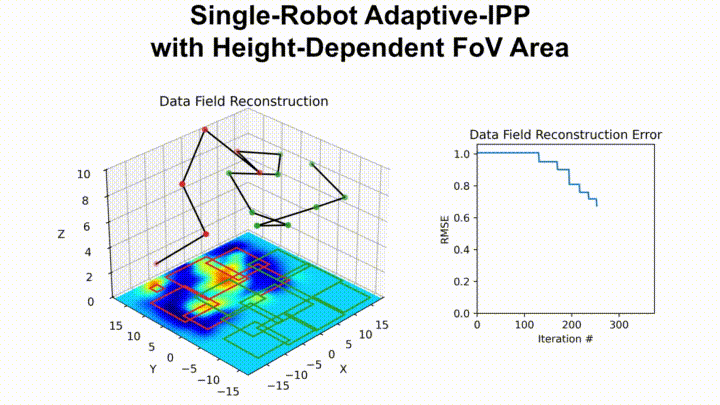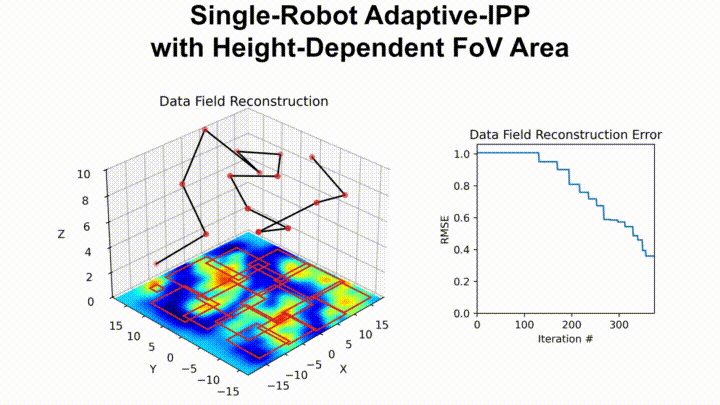
The following shows our path planner adaptively planning a path for an aerial drone with a downward-facing camera tasked with surveying a given area:
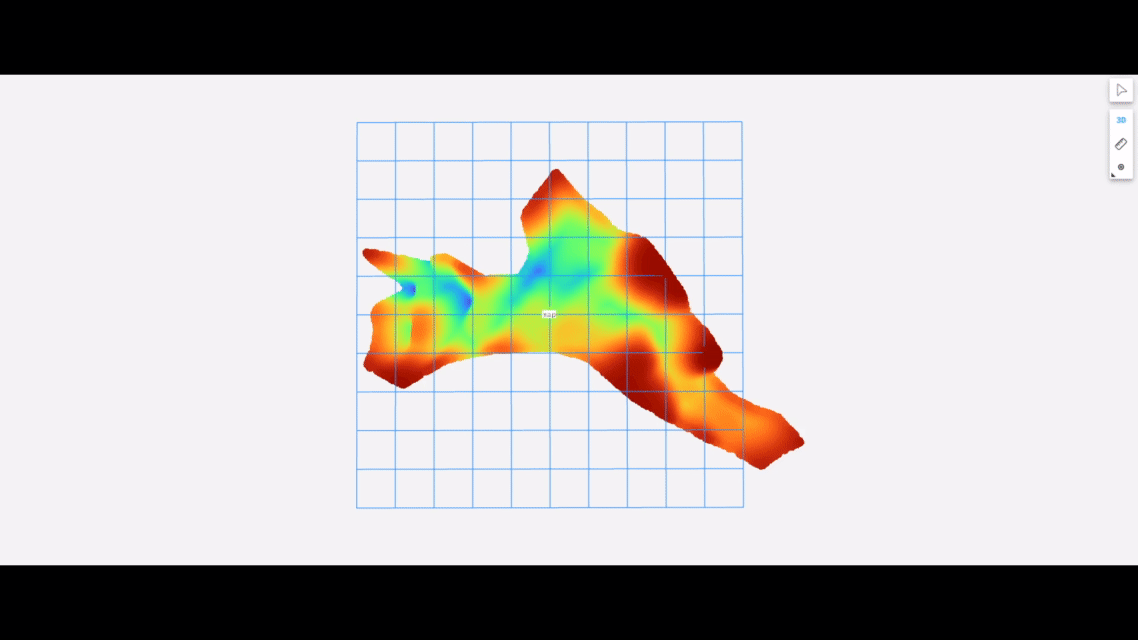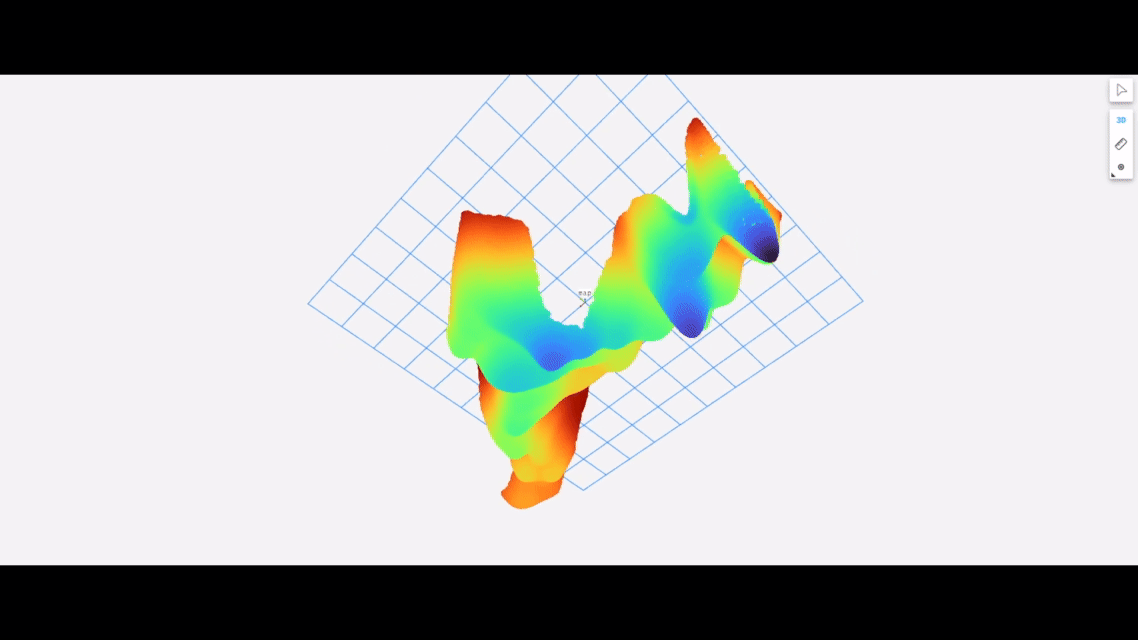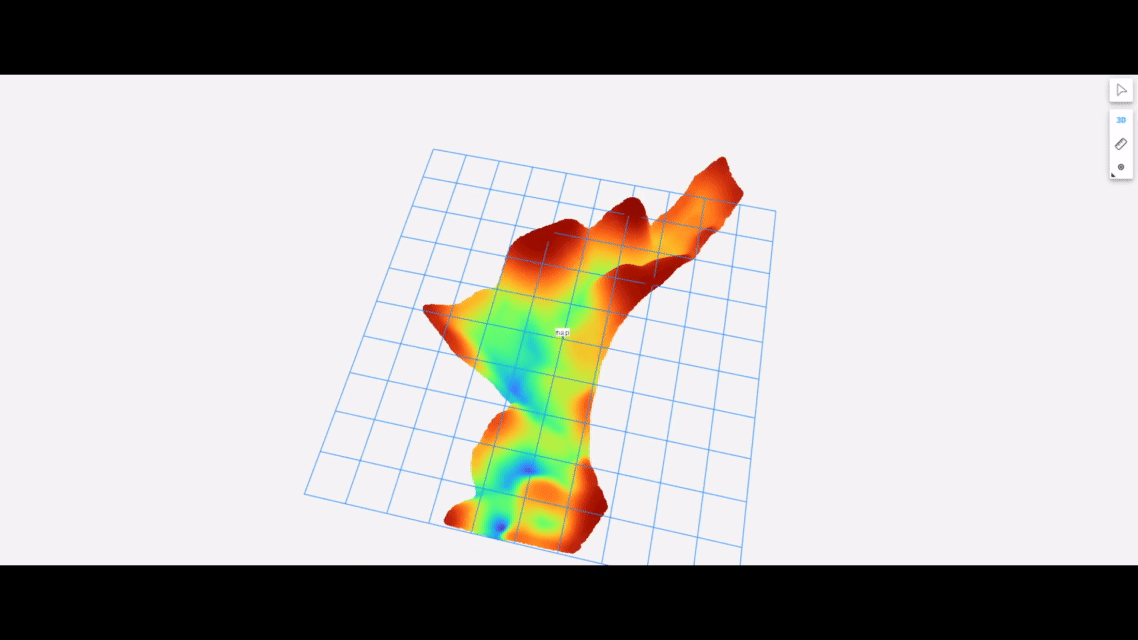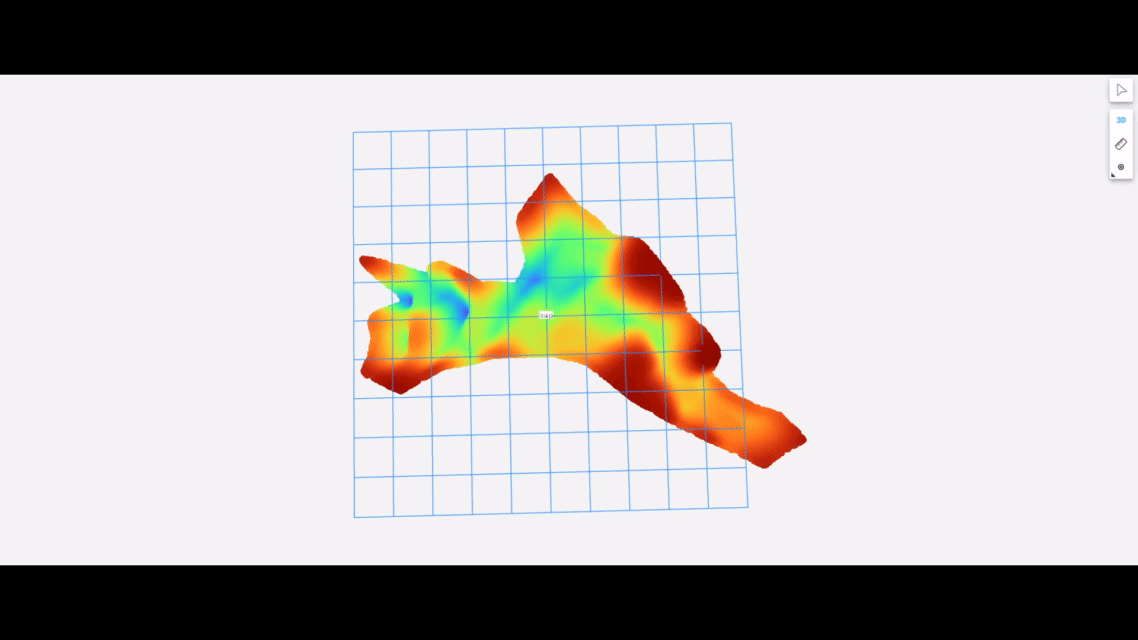
The following shows the underwater terrain estimated using data collected by our package running on an autonomous surface vehicle equipped with the Ping1D sonar:
Setup
-
This extension works only on 64-bit operating systems. You can get the 64-bit image of BlueOS for Raspberry Pi from here.
-
The extension requires over 4GB of memory+swap. Please ensure that the swap size is large enough to accommodate the extension. The extension will copy the shell script
config_swap.shto/usr/blueos/extensions/sgptools/folder on the underlying device. You can use this script to increase the swap size before starting the path planner.You will have to use
Pirate Modeto access BlueOS's built-in terminal and run the script on the underlying device via thered-pillutility. Use the following commands to enablered-pilland increase the swap size:
Usage
Starting a Mission
-
First, we need to define the survey area and the robot launch location. The extension can read this data from QGC plan files. The survey area and launch position must be defined using a polygon-shaped geofence drawn in QGC and saved as
mission.plan.
-
Once you have the plan file, copy it to the robot using the
File Browserfeature in BlueOS'sPirate Mode. Themission.planfile should be uploaded to the following directory:/extensions/sgptools/Once the
mission.planfile is uploaded, restart the extension to ensure that the new file is used for the mission.
-
Finally, use the terminal provided by the SGP-Tools extension to start the mission with the following command:

Viewing the Data after a Mission
The sensor data, along with the corresponding GPS coordinates, will be logged to an HDF5 file in the DATA_FOLDER, where the mission.plan was uploaded.
We can estimate the bathymetry of the entire survey area using the collected data and visualize a normalized version with the following command:
⚠️ Do not run this during the mission, as it will disrupt the path planner
The above command will publish a point cloud that can be viewed using foxglove. You can access it from a web browser at https://app.foxglove.dev/. Use the open connection feature and change the address from localhost to the IP address of the ASV.
You can control the point cloud density using the num_samples parameter. You can set this from foxglove's Parameters panel.
By default, the latest mission log will be visualized. You can visualize a specific mission log using the following command (replace <log folder name> with the log folder name):
Simulator
You can test your mission or develop new algorithms in our companion ROS2/Gazebo simulator
Parameters
You can control the following extension parameters by running the following command in the terminal provided by the SGP-Tools extension:
The parameters reset to their default values after rebooting. They can be made permanent by configuring the parameters using the app environment variables on the BlueOS extensions page in pirate mode.
Available Parameters:
-
PING1D_PORT(default: /dev/ttyUSB0):- Specifies the device to which the Ping1D sonar is mounted. You can get the device port from the
Ping Sonar Devicespage in BlueOS.
- Specifies the device to which the Ping1D sonar is mounted. You can get the device port from the
-
NUM_WAYPOINTS(default: 20):- The number of waypoints optimized by the path planner.
- Increasing the number of waypoints results in a more complex path that covers a larger area.
- Recommend increasing only when the default setting results in a poor reconstruction of the environment, as this increases the computational cost and leads to slower online path updates.
-
SAMPLING_RATE(default: 2):- The number of points to sample along each edge of the path during path planning. The default value of
2means that only the vertices of the path are used. - The path planner assumes the data is collected only at the sampled points. Increasing the sampling rate allows the planner to better approximate the information along the entire path, thereby resulting in more informative paths.
- Recommend increasing only when the default setting results in a poor reconstruction of the environment, as this increases the computational cost and leads to slower online path updates.
- The number of points to sample along each edge of the path during path planning. The default value of
-
KERNEL(default: RBF):- The kernel function used in the IPP approach for online IPP updates. Currently available options:
RBF,Attentive, andNeural - The default
RBFstationary kernel function is fast enough to run on a Raspberry Pi 4. The non-stationary kernel functionsAttentiveandNeuralcan result in more informative paths but require more computational power. - Recommend using a non-stationary kernel only when running BlueOS on a high-performance SoC, such as the Nvidia Jetson platform.
- The kernel function used in the IPP approach for online IPP updates. Currently available options:
-
DATA_BUFFER_SIZE(default: 200):- The number of sensor data samples to collect before using the data to update the model parameters, which, in turn, will be used to update future waypoints.
- Increasing the buffer size will allow the planner to compute better parameter estimates, which will result in more informative paths.
- Recommend increasing only when the default setting results in a poor reconstruction of the environment, as this increases the computational cost and leads to slower online path updates.
-
TRAIN_PARAM_INDUCING(default: False):- Enables training the inducing points of the parameter model (sparse Gaussian process) in addition to the kernel parameters during the path update.
- Enabling this feature will result in more accurate parameter estimates and more informative paths.
- Recommend increasing only when the default setting results in a poor reconstruction of the environment, as this increases the computational cost and leads to slower online path updates.
-
NUM_PARAM_INDUCING(default: 40):- The number of inducing points used in the parameter model (sparse Gaussian process).
- Increasing the number of inducing points will result in more accurate parameter estimates and more informative paths.
- Recommend enabling only when the default setting results in a poor reconstruction of the environment, as this increases the computational cost and leads to slower online path updates.
-
ADAPTIVE_IPP(default: True):- Enables adaptive informative path planning.
- When enabled, it uses the data streaming from the sonar to learn the correlations in the underwater bathymetry and further optimizes the future waypoints to collect even more informative data.
- Recommend disabling it if the onboard sonar is currently unsuppored by this package.
-
NAMESPACE(default: robot_0):- ROS2 namespace, useful when multiple ROS2 robots are operating on the same network.
- Currently, only the single robot planner is fully supported.
-
DATA_TYPE(default: Ping1D):- Type of sensor to be used by the path planner.
- Currently, only the BlueRobotics Ping Sonar is supported.
-
FCU_URL(default: tcp://0.0.0.0:5777@):- URL of the flight controller. This should only be changed if running the package on a non-BlueOS platform.
Disclaimer ⚠️
This extension, when executed properly, will take control of the ASV and could potentially collide the vehicle with obstacles in the environment. Please use it with caution.
About
Please consider citing the following papers if you use this extension in your academic work
@misc{JakkalaA23SP,
AUTHOR={Kalvik Jakkala and Srinivas Akella},
TITLE={Efficient Sensor Placement from Regression with Sparse Gaussian Processes in Continuous and Discrete Spaces},
NOTE= {Preprint},
YEAR={2023},
URL={https://www.itskalvik.com/research/publication/sgp-sp/},
}
@inproceedings{JakkalaA24IPP,
AUTHOR={Kalvik Jakkala and Srinivas Akella},
TITLE={Multi-Robot Informative Path Planning from Regression with Sparse Gaussian Processes},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, {ICRA}},
YEAR={2024},
PUBLISHER = {{IEEE}},
URL={https://www.itskalvik.com/research/publication/sgp-ipp/}
}
@inproceedings{JakkalaA25AIPP,
AUTHOR={Kalvik Jakkala and Srinivas Akella},
TITLE={Fully Differentiable Adaptive Informative Path Planning},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, {ICRA}},
YEAR={2025},
PUBLISHER = {{IEEE}},
URL={https://www.itskalvik.com/research/publication/sgp-aipp/}
}
Acknowledgements
This work was funded in part by the UNC Charlotte Office of Research and Economic Development and by NSF under Award Number IIP-1919233.
License
The SGP-Tools software suite is licensed under the terms of the Apache License 2.0. See LICENSE for more information.
