Bayesian Sensor Placement for Multi-source Localization of Viruses in Wastewater Networks
Abstract
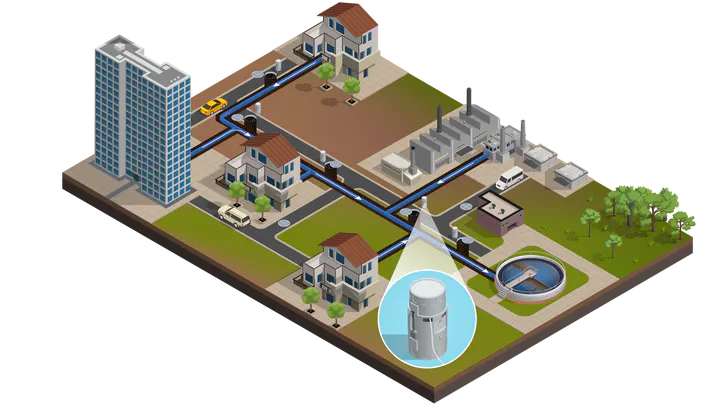
Wastewater monitoring is effective in the early detection of viral and bacterial disease outbreaks. It has recently been used to identify the presence of individuals infected with COVID-19. To monitor large communities and accurately localize buildings with infected individuals, one must choose a specified number of sampling locations in wastewater networks. We model this as a sensor placement problem. Although sensor placement for source localization arises in numerous problems, most approaches use application-specific heuristics and fail to consider multiple source scenarios. We instead develop a Bayesian approach to find informative sensor placements and accurately localize the sources of viruses. Since the resulting optimization problem is NP-hard, we use a greedy approach to generate solutions. Our method finds sensor placements to accurately identify sources of viruses and incorporate minimum virus concentration requirements. Since infection transmission rates can vary between buildings, we demonstrate the robustness of our approach to discrepancies in the infection transmission rate model.
Type
Publication
In Computing Research Repository (CoRR 2022)